International Relations Class 13
AUKUS (AUSTRALIA, UK, USA) (5:10 PM):
- The United States announced on 15 September 2021 that the US and the UK will help Australia acquire nuclear-powered submarines.
- It is a security grouping to contain China.
- Under it, the USA has agreed to share sensitive nuclear submarine technology with Australia, and not with others.
- QUAD will continue as a plurilateral grouping with a vision for a free, open, transparent, and inclusive Indo-Pacific.
- This augurs well for India since India was reluctant to militarily balance China under the Quad.
Next Chapter of AUKUS:
- It was announced in September 2022.
- Britain has plans to make fighter submarines that will be nuclear-powered.
- Britain would share its plans with Australia under SSBN- Sub-Surface Ballistic Nuclear.
- The USA would share the Vertical Launching System(VLS) with both the UK and Australia.
- It is a set of vertical tubes to store missiles.


- More number of missiles and greater payloads can be situated on the submarine.
- These submarines will reach Australian ports by 2047.
- Till 2047, both the USA and the UK will lease out nuclear submarines to Australia.
- These actions will not result in proliferation because they deal with nuclear-powered submarines and not nuclear warheads.
- This is an unprecedented agreement as only two other countries lease out nuclear-powered submarines- Russia and India.
Challenges for the next chapter of AUKUS:
- Since the agreement is very long, it has to pass through various political & economic environments in three countries for a long time.
- SSBNs are very expensive to manufacture.
- The USA itself is struggling to manufacture SSBNs.
- Australia would need to double its strength of existing personnel to man the new SSBNs.
AMERICAN BENEFITS FROM SHARING THE HALLOWED TECHNOLOGY WITH AUSTRALIA (5:40 PM):
- The USA expects to gain more allied firepower.
- The USA would get access to more ports in the Pacific Ocean.
- The USA would gain economies of scale in the manufacturing of SSBNs.
Benefits to Australia:
- Australia will align more closely with the USA against China.
- Australia does not face direct territory threat from China, but Australia seeks open Indo-Pacific routes.
- Australia will be saving considerable time and capital by getting the coveted technology.
- Australian missiles could target the Chinese mainland.
Benefits to the UK:
- It will give a major boost to its struggling shipyard industry.
France:
- Both India and France were considerate of the exclusion of France from the arrangement.
- France and India reached out to each other after the AUKUS commitment to Australia.
- France assured India to strengthen India’s strategic autonomy including its Industrial and technological base as a part of their close relations.
Concerns regarding the sharing of the technology with Australia:
- It was thought that AUKUS could lead to the beginning of an arms race in the Pacific.
- Actually, the arms race began earlier with China taking a large lead.
- China manufactured 12 nuclear submarines in the last 15 years, a feat that even the USA is incapable of.
- AUKUS can be seen more as a reaction to Chinese actions.
India-USA trade relations:
- India- USA bilateral trade has grown over the past many years.
- India enjoys a trade surplus with the USA.
- Despite this, there is a large number of trade disputes between India and the USA in WTO.
India-USA cooperation for counter-terrorism:
- After the USA's withdrawal from Afghanistan, the utility of Pakistan has decreased for the USA.
- Indian efforts to get terrorists like Masood Azhar, to get listed under the UNSC 1267 Committee were put on technical hold by China.
- India was successful in 2019 after the resolution was co-sponsored by India and the USA.
CHALLENGES IN INDIA-USA RELATIONS(6:00 PM)
Trade factor:
- General System of Preferences- The USA gave liberalized market access to certain goods.
- India pushed out after 2020.
- Trump called India a “Tariff King”.
- India objects to the non-tariff barriers put over Indian exports by the USA.
- India objects to the strict labeling requirements (mentioning details about each and every ingredient present) imposed on Indian exports.
- Other issues are disagreements related to TRIPS and H1 B visas.
Russia factor:
- The Russia-Ukraine war saw many sanctions and resolutions that were sponsored by the USA.
- The USA has consistently provided arms to Ukraine.
- India has not condemned and has increased crude purchases from Russia.
- There was also a threat of sanctions on India under CAATSA for the Indian purchase of the S-400 missile defense system.
- Russia remains our primary defense supplier and can be very helpful in conflict with China.
Pakistan factor:
- Kashmir was regarded as a “disputed area” by the USA many times.
- A $ 450 million sustenance package for F-16 fighter jets was signed in 2022.
- The USA announced that the aid is to counter terrorists, but India believes that it will be used against India as in the Balakot airstrike.
- The deal is also a symbolic detente in USA-Pak relations after the Trump Af-Pak policy.
- Under the policy, Pakistan was to play a crucial role in maintaining continuous supply lines for U.S. troops deployed in Afghanistan until their removal.
Way Forward for India-USA relations:
- Despite some irritants, USA-India relations are expected to get stronger.
- American foreign policy has been associated with "fickleness", as it changes very rapidly.
- This is because the USA is a very pragmatic nation.
- Whenever its interests shift, its foreign policy reorients very quickly.
- For example, in response to the crude dependency, the USA provided a security umbrella to the Middle East region.
- After the shale gas discovery, the USA started receding from the Middle East.
- Hence, India cannot trust the USA as much as it trusts Russia.
- The present American interest in India is mainly because India is more reliable against China than its European allies.
- There is a unidirectional nature in India-USA relations.
- The USA is the sole source of investments and driver of strategic relations.
- Under the expansion of SCO and BRICS, the world is moving towards de-dollarization.
Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF):
- Member countries- United States, India, Australia, Brunei, Fiji, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam
- It is not a traditional trade deal and therefore the associated skepticism as to what it will deliver.
- It represents the idea of an “Alternative Trade Arrangement” led by the USA.
The four pillars under IPEF:
- Connected Economy- Setting standards for digital trade, cross-border data flow, and data localization.
- Resilient Economy- Supply chain commitments and guarding against sudden price spikes.
- Clean Economy- Commitments to the clean economy, decarbonization, and infrastructure to cut emissions.
- Fair Economy- In terms of enforcing regimes that cut down on money laundering and corruption, and ensure fair taxation.
- Thus, IPEF is about standard setting and facilitating trade.
- It will not negotiate and lower tariffs or greater market access for its members.
- As negotiations proceed, more areas of cooperation may be incorporated.
- There is an option for members to adopt a Pick and Choose attitude- countries can join only those pillars that interest them.
- India has withdrawn from the trade pillar due to its underdeveloped manufacturing sector.
- India can join this pillar in the future.
- This concept has been developed to attract more members, but it raises questions about the effectiveness of the framework.
Why USA has gone for IPEF:
- It was out of the Comprehensive & Progressive Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) in 2017, and since the USA is not a part of RCEP.
- It is a part of the USA’s Foot in door policy.
- Under this policy, the U.S. wishes to signify that despite its attention to the China and Ukraine conflict, it is still observing the Asia-Pacific region.
INDIA-CENTRAL ASIA RELATIONS (6:35 PM):
Importance of Central Asia:
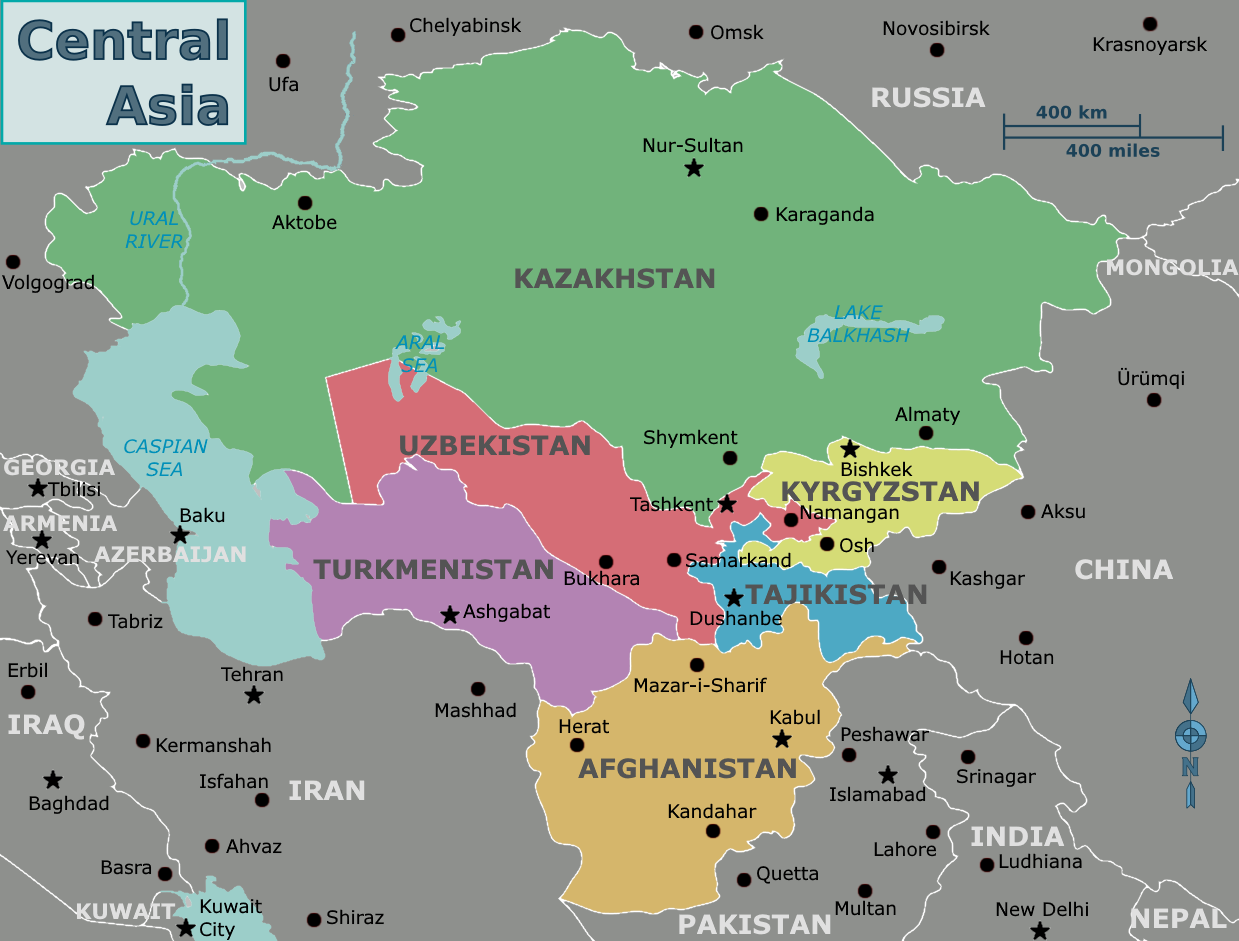
Location:
- Its location is such that Great Games between great powers have been fought on its soil.
- Presently it is an arena of “great game” played out between Russia, China, the USA, Turkey, Iran, Europe, Pakistan, and India.
- They act as a gateway to Europe, East Asia, and West Asia.
- Geo-political theorist Mackinder who gave the theory of heartland discussed the importance of the Eurasian Heartland comprising Central Asia.
- According to him, those who rule the heartland will rule the world.
- The region was located on the ancient Silk Route -3rd BCE to 15th AD, so it is important to Chinese BRI.

Economic importance:
- Kazakhstan is the predominant power in the region, holds the world’s second-largest natural reserves of Uranium, and largest producer of uranium.
- Uzbekistan- Reserves of Uranium, Natural Gas, and other minerals.
- Turkmenistan- It has the fourth largest natural gas reserves.
- Tajikistan- Huge hydropower potential.
- Kyrgyzstan- Gold and hydropower potential.
- The region represents a "near abroad" market for India.
- It provides alternative overland routes to resource-rich Russia and the Middle East.
- It can be a source of significant energy supplies at relatively shorter distances.
Security:
- The region potentially acts as a buffer to contain the fallout of fundamentalism.
- To insulate India from narco-terrorism and to forestall India’s encirclement by any regional or outside power.
- Narco-terrorism simply means the arrangement where the proceeds from the illegal narcotics trade are used to fuel terrorism.
- The region’s importance has been accentuated after the Taliban’s takeover of Afghanistan, and the threat of the spread of narco-terrorism.
- Good relations with Central Asia will prevent the northern encirclement of India.
Why is India important to Central Asian Republics(CAR) ?:
- CARs since their independence in 1991 have followed a multi-vector foreign policy against their traditional hegemon Russia and their new hegemon China.
- Relations with India augment their strategic maneuverability.
- They want to learn from the Indian experience how to insulate their youth from radicalism.
- Considering the population and the fact that radicalized lone-wolf attacks have reached the USA, Europe, and even Scandinavian countries, India has been remarkable in curbing radical Islam.
- To seek cooperation vis–a–vis Afghanistan, since we intend similar outcomes and share a common vision with respect to peace and security in Afghanistan.
- Inda is seen as a balancing and non-threatening power.
- CARs supported the India-sponsored UNSC resolution 2593.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 2593:
- It was adopted on August 30, 2021, following the fall of Kabul and the subsequent Taliban takeover in Afghanistan.
- According to the resolution, the Security Council demands that Afghan territory not be used to threaten or attack any other country or to shelter and train terrorists.
EVOLUTION OF INDIA-CAR RELATIONS(7:05 PM):
Historical relations:
- India and Central Asia share significant cultural civilizational and historical linkages.
- Central Asia was located on the Silk Route.
- The Silk Route in addition to goods(silk, spices, etc.) served as an effective channel for thoughts, religion, and philosophy.
- Buddhism spread through this route from India to Central Asia(Xinjiang), while Sufism spread from CAR to India.
- Babur came from the Ferghana Valley in Central Asia to establish the Mughal Empire in India.
Soviet period:
- India shared close ties through music, movies(Bollywood & Raj Kapoor), dance, and literature.
1991-2001:
- Post disintegration of the USSR, India had an opportunity to pursue close economic and strategic cooperation with the newly independent.
- However, India was caught up in its domestic economic turmoil.
- In foreign policy, it prioritized befriending the then-single superpower USA.
- However, to strengthen our relations with the region, India launched the “ Look North Policy” in 1995, but it was a non-starter.
- India continued to look at this region from a security perspective.
- For instance, Tajikistan was caught in a civil war this time.
- It is only two decades later that India once again launched the “Connect Central Asia” policy in 2012.
- It emphasized building political, economic, security, and cultural connections.
- However, a major push to the bilateral relations came with PM Modi’s visit to all five Central Asian republics in 2015.
- Since then, our relations have come a long way.
- In 2019, India- Central Asia Dialogue Mechanism was established under which three foreign-ministers-dialogues have taken place.
- The third dialogue emphasized the four C’s- Contact, Connectivity, Commerce & Capacity Development.
- Recently in January 2022, the first India-Central Asia summit was hosted by India in a virtual format.
- It has led to the institutionalization of the relations.
- In a historic decision, they decided to hold the summit every two years.
- India-Central Asia secretariat would be set up in New Delhi.
- India-Central Asia parliamentary forum will be set up to enable robust discussions among the parliamentarians of these countries.
- There are growing convergences and consolidation of the ties.
Geographical facts of the region:
- The Amu Darya and the Syr Darya are the important rivers of the area.
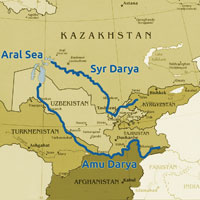
- Russia shares borders only with Kazakhstan among the CAR.
- The Wakhan corridor separates Pakistan from CARs.
- Uzbekistan is a double landlocked country.
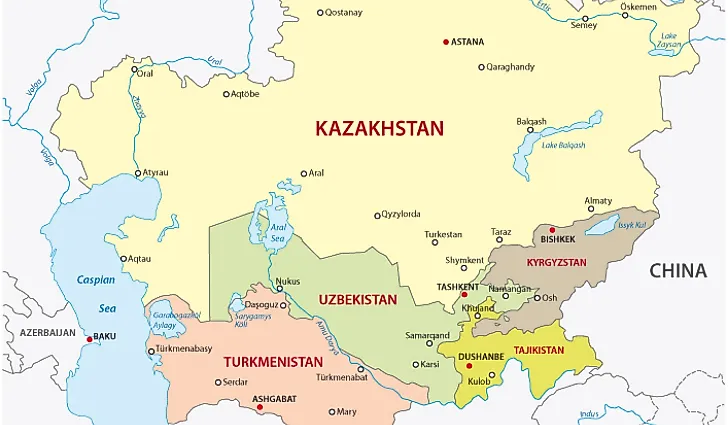
- The Caspian Sea is an important water body in the region.
- The Caspian Sea is bordered by Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, Russia, Iran, and Kazakhstan (TARIK).

AREAS OF COOPERATION (7:30 PM):
- Connectivity:
I. International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) corridor:
- It will be from Jawahar Lal Nehru port to Bandar Abbas via the Caspian Sea to Moscow and St Petersburg.
- It is a 7200 kilometers long multimodal network of ships, rail, and road routes for the transport of goods from India to Russia and Europe.
- Its operationalization is still incomplete.
- The original agreement was signed in 2000 in St. Petersburg by Iran, Russia, and India.
- Since then 10 other countries have joined the agreement.
- Bulgaria has been included as an observer country.
- Two Baltic countries- Latvia and Estonia have expressed their intention to join the agreement.
- This corridor reduces the distance by 40% and costs by 30%.
- It brings down the transit time from 40 days by more than half.
- In June 2021, the western corridor of INSTC was operationalized.

II. TAPI (Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, India) project:
- It seeks to deliver gas from the Galkynysh Gas Field, Turkmenistan.
- It will pass through Herat in Afghanistan, with an extension to Nimruz, Kandahar.
- In Pakistan, it will pass through Quetta, Dera Ghazi Khan, and Multan.
- It will reach India at Fazilka, Punjab.

III. Ashgabat Agreement:
- The Ashgabat agreement is a multimodal transport agreement between the governments of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Iran, Pakistan & Oman.
- The aim was to facilitate the transportation of goods between Central Asia & the Persian Gulf.
- The agreement came into force in April 2016.
- The agreement was originally signed by Iran, Oman, Turkmenistan & Uzbekistan in 2011
- Qatar withdrew in 2013.
Country Granted membership in the Ashgabat Agreement Kazakhstan 2015 Pakistan 2016 India 2018
IV. Development of Chabahar Port:
- The port can enable India to access central Asia through Iran.
V. India- Iran-Uzbekistan Trilateral Agreement 2020:
- The aim is to develop a transportation corridor around the Chabahar port.
Security:
- There is a convergence between India and central Asia regarding the security of the region.
- It was seen for resolution 2593, narco-terrorism, etc.
- India and CARs emphasize the need to strengthen UN-led global cooperation to counter-terrorism.
Energy:
- While Central Asia is richly endowed with energy resources such as coal, oil, natural gas, uranium, etc., India needs resources for growth.
- So there is a considerable scope for energy cooperation.
- All the CARs have shown interest in the Indian initiative of One Sun-One World-One Grid.
- The initiative aims to promote grid connectivity for harnessing solar energy.
Health:
- Indian vaccine diplomacy.
- India has proposed the One Earth, One Health initiative under India-Central Asia relations.
Challenges in India: Central Asia relations:
Low volume of bilateral trade:
- India’s annual bilateral trade with the region stands at $ 2 billion.
- In comparison, India's annual trade is around $ 5 billion.
- Chinese annual trade with CARs is at $40 billion.
Reasons for less trade:
- Despite it being a land-locked region, India lacks over-land connectivity with the region.
- The shortest land route to it passes through hostile Pakistan and unstable Afghanistan.
- Thus, presently India’s trade with the region is conducted through China, even with whom we don't share very cordial relations.
- India’s failure to develop infrastructure projects abroad to foster regional connectivity., for example- Chabahar port in Iran, TAPI, INSTC, etc
China in Central Asia:
Pieces of evidence:
- China is one of the leading trade partners of the region with bilateral trade of around $40 billion.
- With the launch of BRI, China has overtaken Russia as the biggest investor in the region.
- All the CARs have well received BRI.
- Presently 20% of Chinese energy needs are met by CARs through west-east pipelines.
- Three of the five CARs share a border with China(Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan).
- India’s pursuit of institutionalization of relations with Central Asia (China’s immediate neighborhood), prompted China to host a virtual meeting with the five CARs in 2020.
- C+ C5 Foreign Ministers meeting mechanism was established in 2019.
- In their recent 2022 virtual summit, they announced the building of a China-Central Asia community with a shared future.
- In 2023, it was organized in Xi'an.
- It resulted in the Xian Declaration.
- They have agreed to organize such a summit once in two years.
- They have declared that China and Central Asia are closely interdependent like “Lips and teeth” and share joy and sorrow.
- Chinese presence in central Asia concerns India because India fears complete encirclement by China.
- China is already present in the Indian Ocean, as well as in South Asian countries.
The topics for the next class are the challenges in China-Central Asia relations, SCO, and India-Russia relations.
1)
Which of the following countries have a coast to the Caspian Sea?
- Armenia
- Georgia
- Azerbaijan
- Kazakhstan
- Uzbekistan
- Turkmenistan
Choose the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a)1, 3, 4, 6 only
(b)3, 4, 6 only
(c)2, 3, 4, 6 only
(d)1, 2, 4, 6 only
2)
Consider the following countries:
1. Azerbaijan
2. Kyrgyzstan
3. Tajikistan
4. Turkmenistan
5. Uzbekistan
Which of the countries mentioned have borders with Afghanistan? (Prelims 2022)
(a)1, 2, and 5 only
(b)1, 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
3)
Consider the following statements regarding Afghanistan as one of the important neighbours of India,
1. The Wakhan corridor lies between Afghanistan and Iran.
2. UNSC resolution 2593 advocated for the evacuation of people from Afghanistan post-Taliban takeover.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a)1 only
(b)2 only
(c)Both 1 and 2
(d)Neither 1 nor 2
4)
Which of the following countries are members of the INSTC (International North-South Transport Corridor)?
- India
- Iran
- Russia
- Kazakhstan
- Kyrgyzstan
Select the correct code from the options given below.
(a)1, 2, and 5 only
(b)1, 3, and 5 only
(c)1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
(d)3, 4, and 5 only
5)
Consider the following nations:
1. Tajikistan.
2. Turkmenistan.
3. Afghanistan.
4. China.
How many of the above nations are connected to the Wakhan corridor?
(a)Only one
(b)Only two
(c)Only three
(d)All the four
6)
Which of the following would be the most accurate desciption of the Vertical Launching System(VLS) that USA will share with UK and Australia ?
(a)It is a system to use the same satelllite kaunc vehicle for multiple launches.
(b)It is a set of vertical tubes to store missiles on nuclrear powered submarines.
(c)It is a system used in accurate long range land based canons.
(d)It is a cluster of wells used for drilling Shale gas.
7)
The Xi"an declaration deals with which of the folloiwng region ?
(a)Pacific Islands
(b)South America
(c)Sahel
(d)Central Asia
8)
Consider the following statements regarding the Next Chapter of AUKUS:
1. Britain would share its plans with Australia under SSBN- Sub-Surface Ballistic Nuclear.
2. The USA would share the Vertical Launching System(VLS) with Australia.
3. This will surely lead to nuclear proliferation in the Pacific region.
How many of the above statements are incorrect?
(a)Only one
(b)Only two
(c)Only three
(d)None of the above
9)
India has seen a much lesser level of Islamic radicalism than the nations with much lesser Islamic populations. What do you think are the reasons behind it ? (150 words/10 marks)
10)
What do you understand by AUKUS ? How can it effect the global position of India ? (150 words/10 marks).
11)
Why do you think the "New Chapter of AUKUS " was signed in 2022 ?(150 words/10 marks)
12)
Why do you think India does not trust USA as much as it trusts Russia ?(150 words/10 marks)
13)
How central Asian countries are important for India? (150 words/10 marks)
Answers
1) b
2) c
3) b
4) c
5) c
6) b
7) d
8) a
It is argued that challenges in India -USA relations are characterized by the involvement of third-party relationships. Comment (10 marks/150 words)
(10 marks)




0 Comments