Doubts are taken for the previous class
- Diagrams and charts are shown for Torque (Refer to the chart) (05: 26 PM)
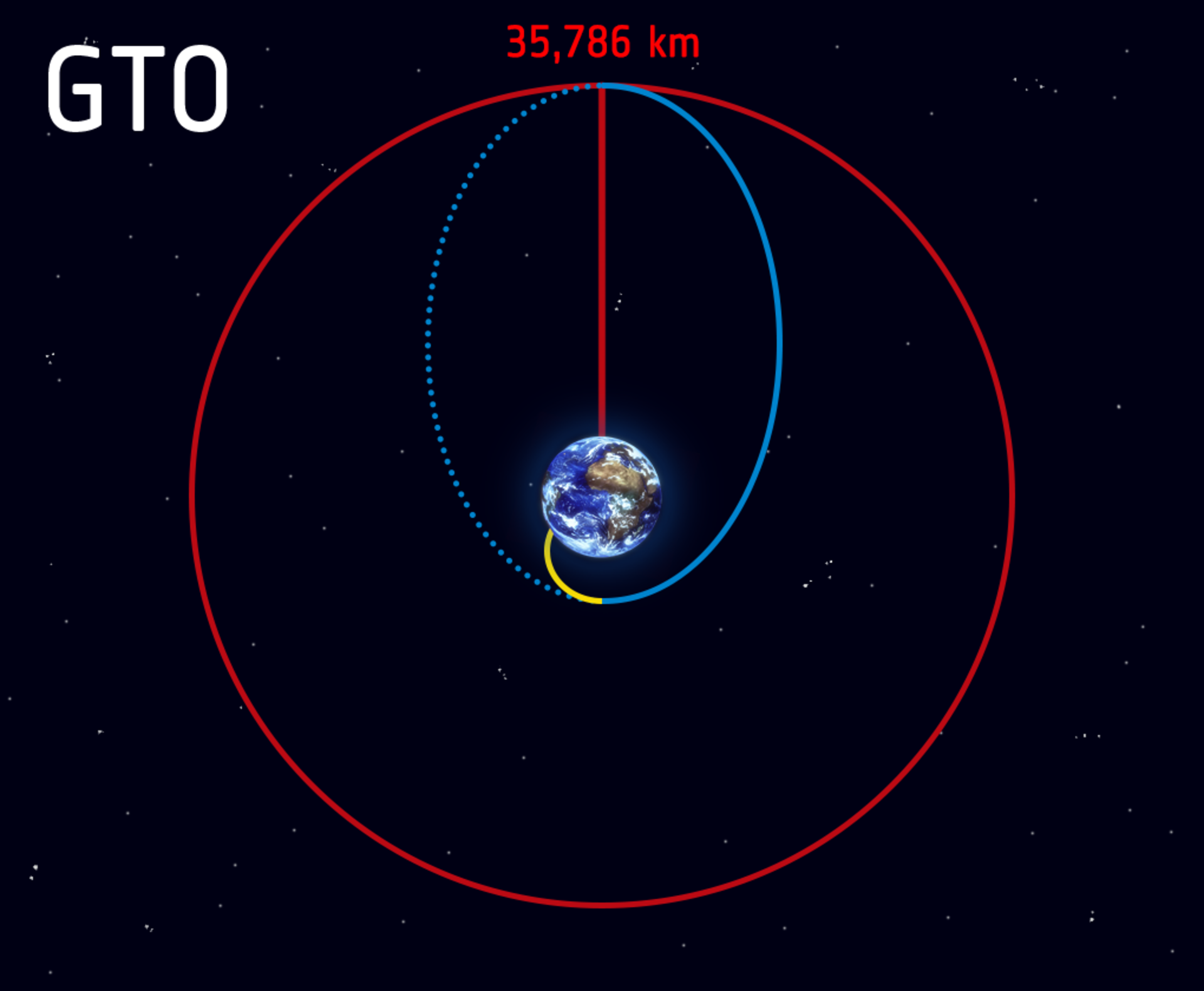
Geo Transfer Orbit
- To attain Geosynchronous or Geo stationery a satellite is first placed into a highly elliptical orbit whose perigee can be very less but the apogee will be in the range of 36000 km.
- When the satellites reach the apogee They can be given a boost so that they can achieve the desirable geosynchronous or geostationary orbit.
- The intermediate orbits are called Geo Transfer orbits.
Sun Synchronous orbit
- In a Sun-synchronous orbit, satellite orientation is fixed relative to the sun throughout the year thus whenever a satellite crosses a point on earth sun's position in the sky is almost the same hence satellite will cross the point earth at the same local solar time.
- This is a very useful characteristic for Earth observation satellites because scientists can collect data across several years and compare the changes for a particular region without worrying about extreme changes in lighting and shadow.
- How to achieve sun synchronous
- Earth is not a perfect sphere because of this satellites orbits often do not remain fixed.
- Orbit in itself starts rotating such type of motion is called precisional motion.
- Generally, the precisional motion of orbits is not desirable.
- In a sun-synchronous orbit, we make it desirable. Erath's position concerning the sun changes also because of Earth's revolution around it. If we can achieve a precision that cancels out the daily change in the position of the sun because of Earth's Revolution we can achieve sun-synchronous.
- It is often achieved at an inclination of 94-96 degrees because of this it is also called a polar sun-synchronous orbit. Height is 500-800 km.
- With one degree of precision every day we can achieve sun-synchronous.
Types of Satellites
- Mainly 3 types of satellites:
- a)Communication satellites
- b)Earth observation or Remotes sensing satellites
- c)Satellite navigation
Communication satellites
- These satellites maintain a communication channel between two points on earth that are far away from each other.
- They are often placed in Geosynchronous/Geostationary orbits.
- ISRO has one of the most extensive communication satellite programs named INSAT in the Asia Pacific region.
- Recently ISRO has changed the nomenclature from GSAT to CMS for communication satellites.
- Applications:
- Radio, Television,
- Education: ISRO under Edusat prog provides satellite-based instructions for free throughout the country.
- Healthcare: With help of satellites Rural hospitals and colleges can be connected to speciality hospitals in cities.
- VSAT (Very small aperture terminal):
- These are Ground stations with small antennas(1-4 meters) that can maintain satellite connectivity and with the help of these stations, we can transfer data from one location to another.
- Cospas-Sansat
- It is a satellite-aided search and rescue program with the help of an emergency beacon an aeroplane or a ship or even a person lost in remote areas can be located. India is a member of this program.
Earth observation satellite
- These satellites with the help of powerful techniques such as Radar imaging synthetic aperture radar, Light detection, and ranging, spectroscopy, and Hyperspectral imaging among others can collect data about a particular region of the earth which can be used to determine physical, Chemical even biological properties for a particular reason.
- It can be useful across many areas such as:
- a)Soil monitoring in agriculture
- b)Geology and geomorphology
- c)Environmental monitoring such as forest
- d)Renewable energy capacity
- e)Ocean sciences
- f)Weather information
- g)Natural resource monitoring
- h)Disaster management
- i)Implementation of Government schemes
- ISRO has dedicated satellites for different objectives recently ISRO changes the nomenclature of satellites and they will be called EOS
- They are generally placed into LEO, Polar sun-synchronous orbit, and sometimes even in Geosynchronous, Geostationary rotations.
NISAR mission
- Record fine Images. It is a remote-sensing technique
- NASA And ISRO have collaborated.
- Objective: Disaster Monitoring and Environmental Monitoring
The topic for the next class: Satellite navigation and Rockets of ISRO




0 Comments