Geography Class 11
Last class revision(5.10 PM).
Isostatcy/Isostatic movements(5.22 PM):
- Isostasy is the state of equilibrium or balance in the earth's crust.
- Isostatic movements involve vertical movements under the action of floatation displacement between the rock layers of differing density and mobility.
- This is to achieve balanced crustal columns of uniform mass above a level of compensation in which the topographic elevation is inversely related to underlying rock density.
- For example, the Mountains have deep roots, like the Scandinavian mountains due to the melting of ice sheets are observing the gradual rising of the land which is evident in a series of raised beaches.
Eustatic movements(5.44 PM):
- They involve the worldwide movement of sea level resulting from changes in the total volume of liquid seawater or capacity of ocean basins.
- The volume of seawater can be changed by melting or the formation of glaciers.
- The capacity of the basin can be changed through the formation of ridges or the expansion of basins.
Continental drift theory(5.55 PM):
- The continental drift theory was proposed by Alfred Wegner(a german meteorologist) in 1912.
- The theory was proposed to explain major variations in the earth's climate.
- Assumptions:
- The three layers of the earth with outer SiAl, intermediate SiMa, and inner NiFe.
- The continental masses were assumed to be floating on oceanic crust without any resistance.
- The Theory:
- Before the Carboniferous period(280-250 million years ago), there was only one supercontinent called Pangea and one superocean called Panthalassa.
- This Supercontinent started to rift during the Carboniferous period.
- It was split into northern Angaraland(Laurasia) and southern Gondwanaland by a rift running east to west.
- Gradually this rift enlarged to form the Tethys Sea.
- The Angaraland consisted of North America, Greenland, and Eurasia without India and Arabia.
- The southern Gondwanaland consisted of Africa, South America, India, Australia, and Antarctica.
- A North-South rift separated North America from Eurasia and South America from Africa which started to move towards the West.
- India started moving toward the North.
- Australia got separated from Antarctica and moved toward the northeast
- Africa moved towards the north.
- Finally, Arabia got separated from Africa and merged into Asia.
- Forces responsible for the continental drift:
- Alfred Wegner proposed the following forces as the cause of continental motion:
- Equatorward or North-South movement is caused by the Pole-fleeing force due to Gravitational differential force and the force of Buoyancy.
- The westward movement is caused by the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon.
Evidence in support of continental drift theory(7.12 PM):
- The diagrammatic representation of pieces of evidence:
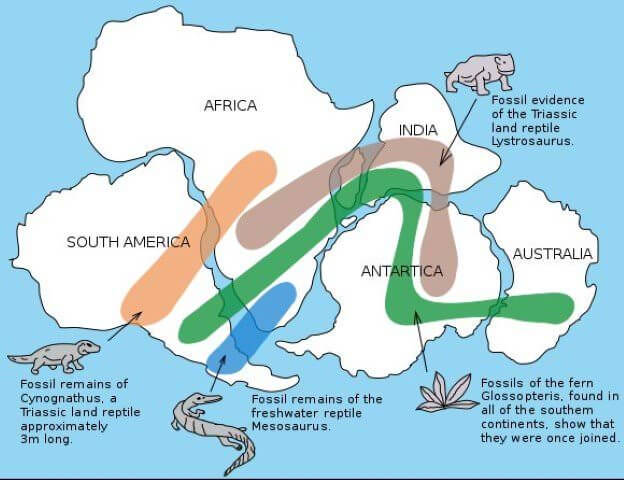
- Justafix or zig-saw fits of continents:
- There are similarities in coastlines on opposite sides of the Oceans.
- All the continents can be merged to form one big continent.
- Structural pieces of evidence:
- The nature of physiography structure in different parts of the continents, having the same age and structural properties
- The mountain belts of Brazil terminate on the South American east coast and the same type of mountains reappeared again in Africa.
- Stratigraphic pieces of evidence:
- The eastern coast of brazil has the same type of rock formations observed along with Northwest Africa.
- Fossil evidence:
- Mosasaurus is an aquatic reptile whose fossil remains are found only in South America and South Africa separated by a wide ocean.
- The fossils of Glossopteeris(a fern) grown only in subpolar climates are now found in warm climatic regions separated by wide Oceans.
- Glacial deposits:
- The layers of tillites are found in warm tropical regions like South America, South Africa, Australia, and India.
- Placer deposits:
- The rich deposits of gold Placer near the Ghana coast without any source of Gold nearby.
Criticisms of continental drift theory(7.44):
- The forces suggested for the movement of the continent are considered to be inadequate.
- The rocks of continental crust and oceanic crust are very rigid and would not permit the drifting of continents over the oceanic floor.
- The theory did not describe the situations of pre-carboniferous times.
Mapping(7.49 PM):
- Africa:
- It is also called the dark continent as it was discovered very late.
- It is home to the largest desert(the Sahara desert).
- It is home to the longest river on the earth that is the Nile river.
- The Nile is made of 2 rivers, the blue and white Nile.
- Mount Kilimanjaro is the highest point in Africa.
- The lowest point in Africa is the lake Assal(in Djibouti).
The topic for the next class: Seafloor spreading and plate tectonic theory.
Images
Here are 40 short answer type questions with answers based
on the notes on Geography Class 11:
1. What is isostasy?
- Isostasy is the
state of equilibrium or balance in the earth's crust.
2. What do isostatic movements involve?
- Vertical
movements under the action of floatation displacement between rock layers of
differing density and mobility.
3. What is an example of isostatic movement?
- The gradual
rising of the Scandinavian mountains due to the melting of ice sheets.
4. What do eustatic movements involve?
- Worldwide
movement of sea level resulting from changes in the total volume of seawater or
capacity of ocean basins.
5. How can the volume of seawater change in eustatic
movements?
- By melting or the
formation of glaciers.
6. How can the capacity of ocean basins change in eustatic
movements?
- Through the
formation of ridges or the expansion of basins.
7. Who proposed the continental drift theory?
- Alfred Wegener, a
German meteorologist, in 1912.
8. What was the purpose of the continental drift theory?
- To explain major
variations in the earth's climate.
9. What are the three layers of the earth according to the
continental drift theory?
- SiAl (outer),
SiMa (intermediate), and NiFe (inner).
10. What is Pangea?
- A supercontinent
that existed before the Carboniferous period.
11. What is Panthalassa?
- The superocean
surrounding Pangea.
12. What did Pangea split into?
- Northern
Angaraland (Laurasia) and southern Gondwanaland.
13. What is the Tethys Sea?
- A rift that
enlarged to form a sea between Angaraland and Gondwanaland.
14. What continents were part of Angaraland?
- North America,
Greenland, and Eurasia (excluding India and Arabia).
15. What continents were part of Gondwanaland?
- Africa, South
America, India, Australia, and Antarctica.
16. What caused the continents to move according to Wegener?
- Pole-fleeing
force due to gravitational differential force and buoyancy, and tidal forces of
the Sun and Moon.
17. What is the 'justafix' or zig-saw fit of continents?
- The similarity
in coastlines on opposite sides of the oceans.
18. What is structural evidence for continental drift?
- Similar
physiographic structures in different parts of continents of the same age and
properties.
19. What is stratigraphic evidence for continental drift?
- Similar rock
formations on the eastern coast of Brazil and Northwest Africa.
20. What is fossil evidence for continental drift?
- Fossils of the
same species found on different continents now separated by wide oceans.
21. What is an example of fossil evidence for continental
drift?
- Fossils of the
aquatic reptile Mosasaurus found in South America and South Africa.
22. What is another example of fossil evidence for
continental drift?
- Fossils of the
fern Glossopteris found in now warm climates but originally grown in subpolar
climates.
23. What is glacial deposit evidence for continental drift?
- Layers of
tillites found in warm tropical regions like South America, South Africa,
Australia, and India.
24. What are placer deposits in relation to continental
drift?
- Rich deposits of
gold near the Ghana coast without any nearby source of gold.
25. What is a criticism of the continental drift theory?
- The forces
suggested for the movement of continents are considered inadequate.
26. Why was the rigidity of rocks a criticism of the
continental drift theory?
- Because the
rigid rocks of the continental and oceanic crust would not permit drifting.
27. What was another criticism of the continental drift
theory?
- It did not
describe the situations of pre-Carboniferous times.
28. What is Africa often called?
- The dark
continent, as it was discovered very late.
29. What is the largest desert in Africa?
- The Sahara
Desert.
30. What is the longest river in Africa?
- The Nile River.
31. What are the two rivers that make up the Nile?
- The Blue Nile
and the White Nile.
32. What is the highest point in Africa?
- Mount
Kilimanjaro.
33. What is the lowest point in Africa?
- Lake Assal in
Djibouti.
34. What is isostatic movement related to?
- The state of
equilibrium or balance in the earth's crust.
35. What type of movement involves changes in sea level?
- Eustatic
movements.
36. What theory explains the movement of continents over
geological time?
- The continental
drift theory.
37. What was the supercontinent called before it split?
- Pangea.
38. What major evidence supports the continental drift
theory?
- Fossil evidence,
structural evidence, stratigraphic evidence, and glacial deposits.
39. What are horsts and grabens associated with?
- Faulting
processes in tectonic movements.
40. What are the two types of tectonic movements?
- Epirogenic
(vertical) and orogenic (mountain-building) movements.
1)
Which of the following is not an epoch of Cainozoic era?
(a)Holocene
(b)Pleistocene
(c)Oligocene
(d)Cambrian
2)
Which of the following is the correct sequence in ascending order of the period with respect to the Geological Time Scale?
(a)Eon->Era->Period->Epoch->Ages
(b)Ages->Era->Period->Epoch->Eon
(c)Ages->Epoch->Period->Era->Eon
(d)Eon->Epoch->Period->Era->Ages
3)
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
- The First trace of life on land was seen in the Silurian period.
- The Mesozoic era is dedicated to the age of dinosaurs.
- The Meghalaya age is the latest age of the Pliocene Epoch.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a)1 and 2 only
(b)2 and 3 only
(c)1 and 3 only
(d)1, 2 and 3
4)
Arrange the following Period of the Palaeozoic Era according to the geological time scale in chronological order
- Cambrian
- Ordovician
- Silurian
- Devonian
- Carboniferous
- Permian
Which of the following is the correct code?
(a)1-2-3-4-5-6
(b)2-1-4-3-5-6
(c)1-2-3-5-4-6
(d)1-3-5-2-6-4
5)
Which of the following is not an indirect source of information of earth"s interior?
(a)Density studies
(b)Temperature and Pressure studies
(c)Meteorite
(d)Volcanic Eruptions
6)
What do you understand by Geomorphology?
(a)It is the study of the physical features of the earth and the process in which those featured are formed.
(b)It is the study of rocks, and of the way they are formed.
(c)It is the study of solar system.
(d)None of the above.
7)
Which of the following gases mainly constituted the first/early thin atmosphere of the earth?
- Hydrogen.
- Helium.
- Nitrogen.
- Oxygen.
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
(a)1 and 3 only.
(b)2 and 3 only
(c)1 and 2 only.
(d)1,2 and 3.
8)
Consider the following statements regarding the evolution of the Earth:
- Between 3000-2500 million years ago, blue-green algae emerged in ocean water which started to release oxygen through the process of photosynthesis.
- By 2000 million years ago ocean was saturated with oxygen and oxygen started flooding the atmosphere and a new atmosphere emerged.
- The oceans were completely formed around 4000 million years ago.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a)1 and 2 only.
(b)2 and 3 only.
(c)1 and 3 only.
(d)1,2 and 3.
9)
Discuss the various direct and indirect sources which throw light on interior of the earth. (150 words / 10 marks)
10)
Give an account of the Geological time scale and associated major life events which occurred. (10 marks/150 words)
Answers
1) d
2) a
3) a
4) a
5) d
6) a
7) c
8) d
Describe the formation of the inner layer of the earth as well as the evolution of the atmosphere and hydrosphere with respect to the origin and evolution of the earth. (150 words/10 marks)










0 Comments